In a nutshell: A brand new cyber menace tactic has emerged, leveraging social engineering to trick customers into infecting their very own methods with malware. Not too long ago highlighted by Malwarebytes, this technique disguises malicious instruments as CAPTCHA requests. In actuality, these information – usually media or HTML-based – are designed to steal private data or perform as distant entry trojans.
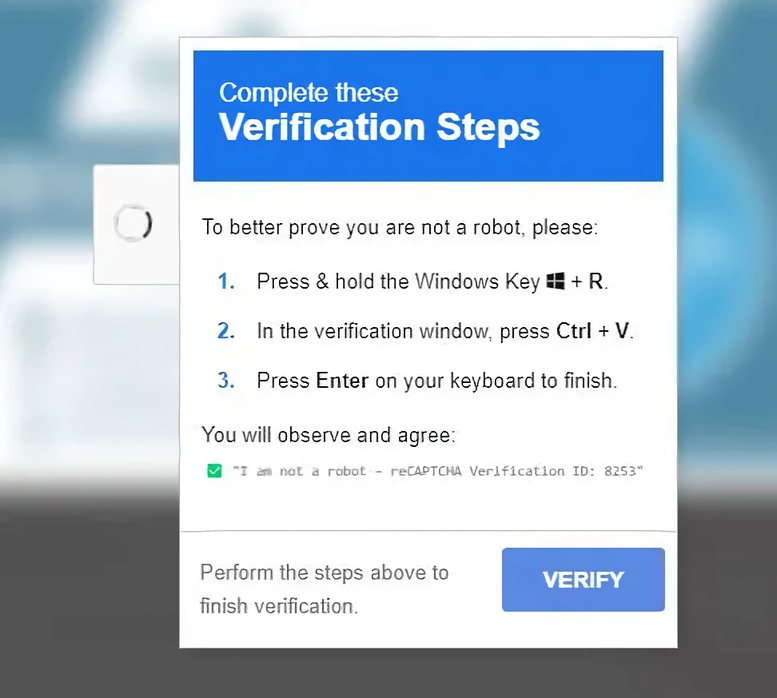
The assault sometimes begins when guests to a web site are prompted to confirm they don’t seem to be robots, a standard follow that not often raises suspicion. Nonetheless, as an alternative of a normal CAPTCHA problem, customers encounter a collection of seemingly innocent steps which are truly a part of a classy rip-off.
The directions may learn: “To higher show you aren’t a robotic, please press and maintain the Home windows Key + R, paste the verification code by urgent Ctrl + V, after which press Enter to finish verification.” These steps are designed to execute a malicious command.
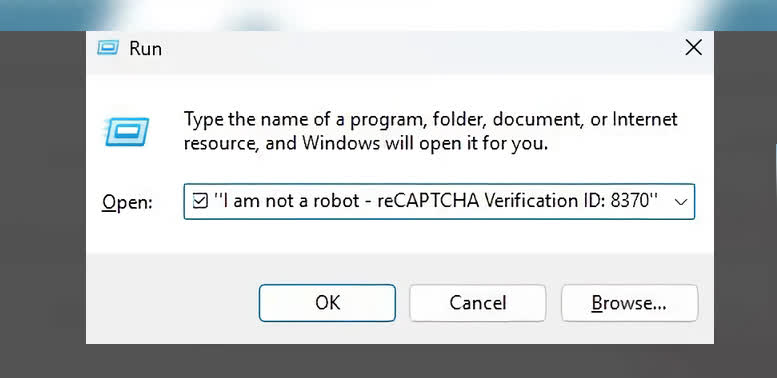
Behind the scenes, the web site makes use of JavaScript to repeat a command to the person’s clipboard. That is potential as a result of, in Chromium-based browsers, web sites can write to the clipboard with the person’s permission. Nonetheless, Home windows assumes this permission was granted when the person checked the “I’m not a robotic” checkbox, creating a possibility for exploitation.
The command pasted into the Run dialog field seems to be a easy verification message however is definitely a set off for the mshta command, which downloads a malicious file from a distant server. This file is commonly disguised as a media file, reminiscent of an MP3 or MP4, however comprises an encoded PowerShell command that silently retrieves and executes the precise malware payload.
The malware payloads utilized in these assaults embody Lumma Stealer and SecTopRAT, each designed to extract delicate knowledge from contaminated methods. The assault is especially efficient as a result of it exploits person belief in CAPTCHA verification processes, posing a threat even to those that are usually cautious on-line.
To mitigate these threats, MalwareBytes advises customers to be cautious of directions from unfamiliar web sites. Utilizing an energetic anti-malware answer that blocks malicious web sites and scripts is important. Moreover, browser extensions that block identified rip-off domains can present an additional layer of protection.
Whereas disabling JavaScript can stop clipboard hijacking, it might additionally disrupt performance on many web sites. A extra sensible method, as beneficial by MalwareBytes, is to make use of totally different browsers for various functions – reserving one particularly for visiting much less trusted websites.



